BD Vacutainer Tubes are essential tools for blood collection, offering precise sample preparation for clinical testing. They ensure accurate test results through specialized additives and vacuum technology.
1.1 Overview of BD Vacutainer Systems
The BD Vacutainer System is a comprehensive blood collection platform designed to enhance accuracy and efficiency in clinical settings. It utilizes vacuum-sealed tubes with specific additives to ensure proper sample preparation for various laboratory tests. The system supports the collection of serum, plasma, or whole blood, catering to diverse diagnostic needs. With a wide range of tube options, including serum, EDTA, citrate, gel, and specialized tubes, the BD Vacutainer System offers tailored solutions for different testing requirements. Its standardized design and precise vacuum technology minimize errors and ensure consistent sample quality. This system is widely adopted in healthcare facilities due to its reliability and adaptability to modern laboratory standards.
1.2 Importance of Proper Tube Selection
Proper tube selection is crucial for accurate laboratory results and patient care. Each BD Vacutainer tube is designed for specific blood components, ensuring correct sample processing. Improper selection can lead to inaccurate test outcomes, requiring retesting and delaying diagnoses. For example, serum tubes are ideal for clot formation and serum separation, while EDTA tubes prevent clotting for hematological tests. Citrate tubes are essential for coagulation studies, and gel tubes aid in serum separation. Specialized tubes, like CPT, are used for cell preparation. Adhering to the recommended order of draw and tube selection guidelines minimizes pre-analytical errors, ensuring reliable and timely test results. This underscores the necessity of understanding and adhering to tube selection protocols.
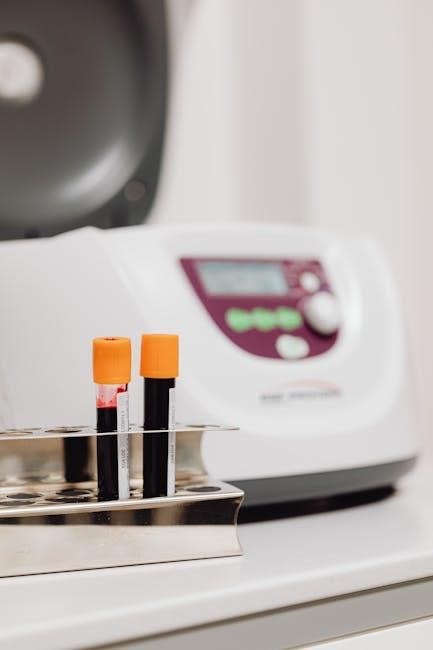
Types of BD Vacutainer Tubes

BD Vacutainer Tubes are categorized by additives, ensuring precise sample collection. Each tube type—serum, EDTA, citrate, gel, and specialized—serves specific clinical testing needs.
2.1 Serum Tubes (Red Tubes)
Serum tubes, commonly known as red tubes, are designed for serum separation and clot formation. They contain a clot activator to accelerate coagulation and may include a gel separator to divide serum from blood cells. These tubes are ideal for clinical chemistry tests, such as liver function, electrolyte levels, and infectious disease screening. Proper handling involves allowing the blood to clot at room temperature for 60 minutes before centrifugation. Centrifuging within two hours ensures accurate test results. Following these steps prevents hemolysis and maintains sample integrity, which is critical for reliable diagnostic outcomes.
2.2 EDTA Tubes (Purple Tubes)
EDTA tubes, recognized by their purple color, contain ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, an anticoagulant that prevents blood clotting by chelating calcium ions. These tubes are primarily used for hematological testing, such as complete blood counts (CBCs), blood typing, and cross-matching. The anticoagulant ensures that blood components remain intact, allowing for precise analysis of red and white blood cells and platelets. Immediate mixing after collection is crucial to prevent clotting and ensure accurate test results. EDTA tubes are widely used in clinical settings for routine blood analyses, making them a fundamental tool in diagnostic procedures.
2.3 Citrate Tubes (Blue Tubes)
Citrate tubes, identifiable by their blue color, are designed for coagulation studies. They contain buffered sodium citrate, which acts as an anticoagulant by binding calcium ions, essential for the clotting process. These tubes are used for tests such as prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT), which measure blood clotting factors. Proper filling is critical, as underfilling can lead to inaccurate results due to an incorrect blood-to-anticoagulant ratio. After collection, tubes should be gently inverted several times to ensure thorough mixing with the additive. Timely processing and centrifugation are also vital to maintain sample integrity and obtain reliable coagulation profiles.
2.4 Gel Tubes (Gold Tubes)
Gel tubes, distinguished by their gold color, are designed for serum separation and clot formation. They contain a gel separator and clot activator, which facilitate rapid clotting and clear serum separation upon centrifugation. These tubes are ideal for various clinical chemistry tests, including glucose, cholesterol, and enzyme assays. After collection, immediate inversion is necessary to mix the clot activator with blood. Centrifugation should occur within two hours to ensure the gel effectively separates the serum from the blood cells, preventing hemolysis and maintaining sample stability. Proper handling is crucial to avoid mixing issues and ensure accurate test results.
2.5 Specialized Tubes (e.g., CPT Cell Preparation Tubes)
Specialized tubes, like the BD Vacutainer CPT Cell Preparation Tube, are designed for specific applications such as cell separation and preparation. The CPT tube contains sodium citrate as an anticoagulant and a Ficoll-Hypaque density gradient medium, enabling the isolation of mononuclear cells. This tube is particularly useful for immunological studies and diagnostic testing. After blood collection, the tube should be inverted gently to ensure the anticoagulant mixes with the blood. Centrifugation is performed to separate blood components into distinct layers, allowing for easy extraction of desired cells. Proper handling and centrifugation are critical to maintain cell viability and ensure accurate results in downstream applications.

Recommended Order of Draw
The recommended order of draw for BD Vacutainer Tubes ensures accurate test results by preventing cross-contamination of additives. Start with blood culture bottles, followed by coagulation, serum, EDTA, and gel tubes.
3.1 Blood Collection Sequence
The blood collection sequence is critical to ensure accurate test results and prevent contamination. The recommended order starts with blood culture bottles, followed by coagulation tubes (citrate), serum tubes (red), EDTA tubes (purple), and finally gel tubes (gold). This sequence prevents additives from interfering with other tubes, ensuring reliable laboratory outcomes. Always follow the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines for the order of draw. Proper adherence minimizes errors and the need for redraws. Using the BD Vacutainer Tube Guide can help healthcare professionals maintain consistency and accuracy in blood collection procedures. Correct sequencing is vital for patient care and diagnostic integrity.
3.2 Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Clinical and laboratory standards play a pivotal role in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of blood collection processes. BD Vacutainer Tubes are designed to meet these standards, providing consistent and high-quality results. Proper adherence to guidelines, such as those set by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI), is essential for maintaining sample integrity. The BD Tube Guide outlines these standards, emphasizing the importance of correct tube selection, order of draw, and handling procedures. By following these protocols, healthcare professionals can minimize errors and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. These standards are fundamental to delivering accurate diagnostic outcomes and maintaining patient safety in clinical settings. Adherence to these guidelines is non-negotiable in modern laboratory practices.
Handling and Mixing Procedures
Proper handling ensures accurate test results. Immediate mixing after collection is critical for additive tubes to prevent clotting or separation issues, requiring gentle inversions for optimal sample preparation.
4.1 Immediate Mixing Requirements
Immediate mixing is crucial for BD Vacutainer tubes to ensure accurate test results. Tubes with additives, such as clot activators or anticoagulants, require gentle inversions to mix evenly. Proper mixing prevents clotting or separation issues, ensuring sample integrity. For example, tubes with clot activators must be inverted 5-10 times to activate the clotting process. Similarly, EDTA tubes need mixing to prevent blood cell clumping. Failure to mix can lead to inaccurate test results, requiring re-collection. Always follow the recommended mixing procedures for each tube type to maintain sample quality and avoid delays in testing. Proper technique ensures reliable laboratory outcomes.
4.2 Consequences of Insufficient Mixing
Insufficient mixing of BD Vacutainer Tubes can lead to inaccurate test results, requiring sample re-collection. Incomplete activation of clotting agents or anticoagulants can cause clotting issues or uneven distribution of blood components. For example, in EDTA tubes, poor mixing may result in altered hematocrit levels, affecting CBC results. Similarly, serum tubes with insufficient mixing may have residual clotting factors, leading to fibrin formation and inaccurate chemistry tests. This can delay diagnostic processes, increasing patient inconvenience and healthcare costs. Proper mixing is essential to ensure reliable laboratory outcomes and maintain patient care standards. Always follow the recommended mixing procedures to avoid these issues.

Tube Inversions and Clot Activators
Tube inversions ensure proper mixing of clot activators with blood, activating additives for accurate test results and preventing clotting issues in samples.
5.1 Ensuring Proper Mixing of Additives
Proper mixing of additives in BD Vacutainer tubes is critical for accurate test results. Tube inversions ensure that clot activators and anticoagulants mix thoroughly with blood. Immediately after collection, invert tubes 5-10 times. This action distributes additives evenly, preventing clotting issues and ensuring optimal sample quality. Insufficient mixing can lead to inaccurate test results, requiring repeat blood draws. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for specific tube types, as mixing procedures may vary. Proper technique guarantees reliable laboratory outcomes and maintains patient care standards. Adhering to these steps is essential for consistent and accurate blood sample processing.

Centrifugation Guidelines
Centrifugation separates blood components effectively. Recommended times vary by tube type, with gel tubes requiring special handling to avoid refrigeration during spinning.
6.1 Recommended Centrifugation Times
Centrifugation times for BD Vacutainer Tubes vary by tube type and laboratory protocols; Generally, serum tubes require centrifugation at 1,000-1,200 RCF for 10-15 minutes. EDTA and citrate tubes typically need shorter spins, around 5-10 minutes, to prevent hemolysis. Gel tubes should be centrifuged at 1,000-1,200 RCF for 10-15 minutes to ensure proper separation of serum from blood cells. It’s crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines, as insufficient centrifugation can lead to inaccurate test results. Always use a swing-bucket centrifuge for consistent results. Refrigerated centrifuges are not recommended for gel tubes to maintain sample integrity. Proper centrifugation ensures clear separation and accurate laboratory testing.
6.2 Gel Tube Centrifugation Notes
Gel tubes require specific centrifugation to ensure proper separation of serum from blood cells; Centrifuge at 1,000-1,200 RCF for 10-15 minutes. Avoid refrigerated centrifuges, as they can cause gel breakdown. Ensure tubes are upright during centrifugation to prevent gel migration. Over-centrifugation may damage the gel barrier, leading to inaccurate results. Proper centrifugation ensures clear separation and maintains sample integrity. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for optimal performance. Correct handling is critical for reliable laboratory testing. Adhering to these protocols ensures accurate and consistent results in clinical settings. Proper centrifugation is essential for maintaining the integrity of the gel barrier and ensuring accurate test outcomes. Always refer to the BD Vacutainer Tube Guide for specific instructions.

Storage and Transportation
Store BD Vacutainer Tubes upright at room temperature, avoiding extreme temperatures. Transport samples securely to prevent breakage and maintain sample integrity during transit to laboratories for analysis.
7.1 Proper Storage Conditions
BD Vacutainer Tubes should be stored upright in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and moisture. The ideal temperature range for storage is between 15°C and 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Tubes containing additives or anticoagulants must be kept in their original packaging to maintain sterility and prevent contamination. Avoid exposing tubes to extreme temperatures, such as those below 0°C or above 30°C, as this may compromise the integrity of the additives. Proper storage ensures the tubes remain viable for blood collection and maintains the quality of the samples for accurate laboratory testing. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for storage to guarantee optimal performance.
7.2 Transportation of Collected Samples
Transportation of BD Vacutainer Tubes requires careful handling to maintain sample integrity. Tubes should be kept upright during transport to prevent additive mixing and contamination. Use protective containers to avoid breakage and exposure to extreme temperatures. Samples should not be subjected to temperatures below 0°C or above 30°C, as this may alter test results. Gel tubes, in particular, should not be transported in refrigerated conditions. Ensure timely delivery to the laboratory, ideally within 2 hours of collection for serum tubes, to prevent clotting issues. Proper transportation practices are crucial for accurate test outcomes and adherence to clinical standards. Always follow manufacturer guidelines for specific tube types.

Troubleshooting Common Issues
Common issues include incomplete tube filling, clotting problems in citrate tubes, and gel separation difficulties. Addressing these requires proper techniques and adherence to manufacturer guidelines for optimal results.
8.1 Incomplete Tube Filling
Incomplete tube filling can occur due to improper needle placement or insufficient venous access. Ensure the needle is fully seated and the tube is held vertically. If underfilled, avoid overfilling, as this may compromise sample integrity. Always adhere to the recommended draw volume, typically within 10% of the tube’s stated capacity. Insufficient filling may lead to inaccurate test results or require re-collection. Proper technique and patient preparation are critical to achieving optimal fill volumes. Consult the BD Vacutainer Tube Guide for specific instructions on handling underfilled tubes and troubleshooting steps to prevent recurrence.
8.2 Clotting Issues in Citrate Tubes
Clotting issues in citrate tubes often arise from insufficient mixing or incorrect filling techniques. Proper inversion of the tube is critical to ensure the anticoagulant mixes evenly with the blood. If clotting occurs, it may lead to inaccurate coagulation test results. To prevent this, always fill citrate tubes to the recommended volume and invert them gently but thoroughly. Improper mixing can cause clot formation, requiring re-collection of the sample. Ensure the tube is filled to the correct level, as underfilling or overfilling can disrupt the anticoagulant-to-blood ratio. Adhere to the BD Vacutainer Tube Guide for specific instructions to avoid clotting issues and ensure reliable test outcomes.
8.3 Gel Tube Separation Problems
Gel tube separation issues can occur due to improper mixing or incorrect centrifugation. Insufficient inversion may prevent the gel from mixing properly with the blood, leading to layering issues. If the tube is not centrifuged within the recommended time or at the correct speed, the gel may not separate effectively, causing inaccurate test results. To resolve this, ensure tubes are inverted 5-10 times immediately after collection and centrifuged according to guidelines. Avoid refrigerating gel tubes before centrifugation, as this can delay separation. Always follow the BD Vacutainer Tube Guide for specific instructions to achieve proper gel separation and reliable laboratory results. Proper handling ensures accurate test outcomes and avoids the need for re-collection.
Proper use and handling of BD Vacutainer Tubes ensure accurate test results and efficient workflows. Adherence to guidelines is key for reliable outcomes in clinical settings.
9.1 Key Takeaways for Effective Use
Proper use of BD Vacutainer Tubes ensures accurate test results and efficient workflows. Always follow the recommended order of draw, and mix tubes immediately after collection. Clot activators and gel separators require specific inversion techniques to function correctly. Centrifuge gel tubes within 2 hours, avoiding refrigerated units. Store samples at room temperature unless otherwise specified. Adhere to filling levels and avoid under- or over-filling tubes. For citrate tubes, ensure proper mixing to prevent clotting issues. Regularly check expiration dates and handle tubes carefully to avoid breakage. Proper labeling and prompt transportation to the lab are critical for reliable outcomes. By following these guidelines, healthcare professionals can optimize blood collection processes and ensure high-quality sample integrity.
